Rational Design of Pt Supported Catalysts for Hydrosilylation: Influence of Support and Calcination Temperature Heterogeneous Catalysis
Main Article Content
Abstract
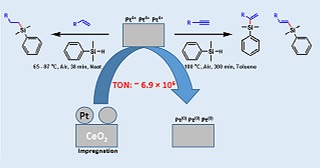
The hydrosilylation reaction plays a key role in organosilicon chemistry, enabling the formation of silicon-carbon bonds crucial for industrial and specialty chemical production. While homogeneous platinum catalysts are incredibly efficient, they come with drawbacks like limited recyclability and high Pt consumption, necessitating researchers to develop more durable, heterogeneous alternatives. By harnessing the synergies of support materials and thermal treatment, this study aims to develop highly active heterogeneous platinum-supported catalysts for the hydrosilylation reaction. We synthesized Pt-supported catalysts on nine different metal oxide supports using impregnation and heat treatment at 500 – 1000 oC. Among them, Pt/CeO2 900H, prepared by calcining Pt-supported CeO2 at 900 °C, followed by reducing it with hydrogen at 500 °C, emerged as the most effective catalyst for alkene hydrosilylation, achieving a turnover number (TON) of 6.9 × 106, comparable to the widely used Karstedt catalyst. For alkyne hydrosilylation, Pt/CeO2 600C and Pt/ZrO2 500C demonstrated outstanding performance. These catalysts, prepared by calcining Pt-impregnated CeO2 at 600 °C and ZrO2 at 500 °C, respectively, exhibited remarkable activity and stability, maintaining high performance over 10 reaction cycles. These findings highlight how the right combination of support material and thermal treatment can fine-tune Pt catalysts for more sustainable hydrosilylation processes. By providing a scalable and cost-effective alternative to traditional homogeneous catalysts, this work connects fundamental research with industrial applications, advancing greener and more efficient approaches to organosilicon synthesis.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
B. Marciniec. Catalysis by transition metal complexes of alkene silylation–recent progress mechanistic implications. Coord. Chem. Rev., 2005, 249, 2374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2005.02.025
L. H. Sommer, E. W. Pietrusza, F. C. Whitmore. Peroxide-Catalyzed Addition of Trichlorosilane to 1-Octene. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1947, 69, 188. https://doi.org/doi:10.1021/ja01193a508
Z. T. Ball, 10.17 - C–E Bond Formation through Hydrosilylation of Alkynes and Related Reactions, Comprehensive Organometallic Chemistry III, Vol. 10 (Eds.: D. M. P. Mingos, R. H. Crabtree). Elsevier Science, 2007, 789-813. https://doi.org/10.1016/B0-08-045047-4/00139-4
G. Pan, C. Hu, S. Hong, H. Li, D. Yu, C. Cui, Q. Li, N. Liang, Y. Jiang, L. Zheng, L. Jiang. Biomimetic caged platinum catalyst for hydrosilylation reaction with high site selectivity. Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 64. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20233-w
L. D. de Almeida, H. Wang, K. Junge, X. Cui, M. Beller. Recent Advances in Catalytic Hydrosilylations: Developments beyond Traditional Platinum Catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 2021, 60, 550. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202008729
K. Kamata, A. Suzuki, Y. Nakai, H. Nakazawa. Catalytic hydrosilylation of alkenes by iron complexes containing terpyridine derivatives as ancillary ligs. Organometallics, 2012, 31, 3825. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/om300279t
I. K. Goncharova, R. A. Novikov, I. P. Beletskaya, A. V. Arzumanyan. Recyclable convenient-to-hle Pt/ethylene glycol catalytic system – an approach to sustainable hydrosilylation. J. Catal., 2023, 418, 70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2023.01.004
T. K. Meister, K. Riener, P. Gigler, J. Stohrer, W. A. Herrmann, F. E. Kühn. Platinum Catalysis Revisited—Unraveling Principles of Catalytic Olefin Hydrosilylation. ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 1274. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b02624
L. W. Chung, Y.-D. Wu, B. M. Trost, Z. T. Ball. A Theoretical Study on the Mechanism, Regiochemistry, and Stereochemistry of Hydrosilylation Catalyzed by Cationic Ruthenium Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 11578. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja034833
J. Heveling. Heterogeneous catalytic chemistry by example of industrial applications. J. Chem. Edu., 2012, 89, 1530. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed200816g
Y. Watanabe, Catalysis of Pt Clusters on Metal Oxide, in Encyclopedia of Interfacial Chemistry, K. Welt Ed. Oxford: Elsevier, 2018, 398-405. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-409547-2.12983-X
T. W. veelen, C. Hernández Mejía, K. P. de Jong. Control of metal-support interactions in heterogeneous catalysts to enhance activity selectivity. Nat. Catal., 2019, 2, 955. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-019-0364-x
Y. Nakajima, S. Shimada. Hydrosilylation reaction of olefins: recent advances perspectives. RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 20603. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra17281g
L. Zhang, M. Zhou, A. Wang, T. Zhang. Selective Hydrogenation over Supported Metal Catalysts: From Nanoparticles to Single Atoms. Chem. Rev., 2020, 120, 683. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00230
X. Cui, K. Junge, X. Dai, C. Kreyenschulte, M. M. Pohl, S. Wohlrab, F. Shi, A. Brückner, M. Beller. Synthesis of Single Atom Based Heterogeneous Platinum Catalysts: High Selectivity Activity for Hydrosilylation Reactions. ACS Cent. Sci., 2017, 3, 580. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.7b00105
Y. Chen, S. Ji, W. Sun, W. Chen, J. Dong, J. Wen, J. Zhang, Z. Li, L. Zheng, C. Chen, Q. Peng, D. Wang, Y. Li. Discovering Partially Charged Single-Atom Pt for Enhanced Anti-Markovnikov Alkene Hydrosilylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 7407. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b03121
C. J. Kong, S. E. Gillil, B. R. Clark, B. F. Gupton. Highly-active, graphene-supported platinum catalyst for the solventless hydrosilylation of olefins. Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 13343. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc07641c
K. Okumura, H. Hoshi, H. Iiyoshi, H. Takaba. Formation of a Pt-MgO Solid Solution: Analysis by X-ray Absorption Fine Structure Spectroscopy, ACS Omega, 2022, 7, 27458. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c02486
M. Hatanaka, N. Takahashi, T. Tanabe, Y. Nagai, K. Dohmae, Y. Aoki, T. Yoshida H. Shinjoh. Ideal Pt loading for a Pt/CeO2-based catalyst stabilized by a Pt–O–Ce bond. Appl. Catal. B, 2010, 99, 336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.07.003
K. Okumura, R. Chihara, A. Abdullahi, M. Kato. Characterization of the active species in the aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol catalyzed by Ru/ZrO2. Mol. Catal. B, 2025, 573, 114820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2025.114820
H. Chuanqing, Y. Yingzhi, Y. Yue, W. Dashan, H. Feiyang, W. Xuewen, Z. Rongbin, F. Gang, Y. Jinmei. Ru/La2O3 catalyst for ammonia decomposition to hydrogen. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 476, 928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.112